Using Azure SQL Server
Connect to database via SSMS
When SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) opens you will be prompted for the connection details.
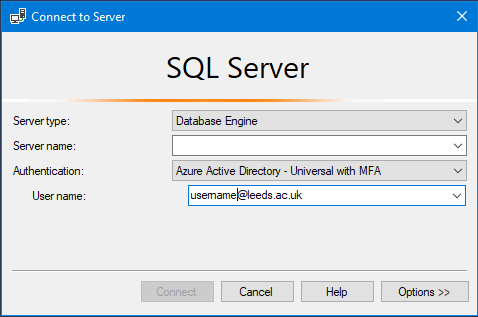
Enter the following:
- Server type = Database Engine
- Server name = <ServerName>.database.windows.net
- Authentication = Azure Active Directory - Universal with MFA
- Username = <username>@leeds.ac.uk
Click ‘Options »’ and go to the second tab ‘Connection Properties’.
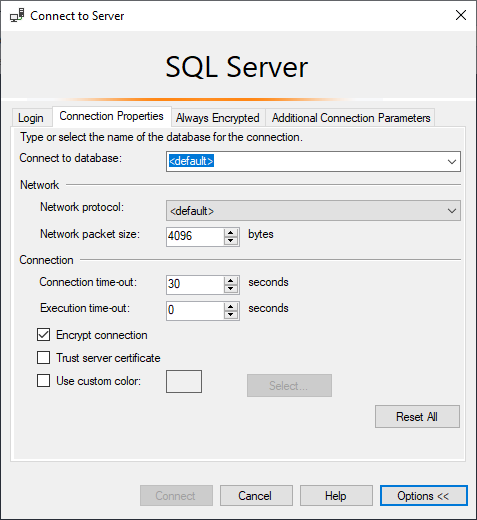
Change ‘Connect to database’ from <default> to the name of your database.
Click ‘Connect’ and your database will appear in the Object Explorer.
Connect to database via ODBC
Your connection string will need to include at least:
- Driver name
- Server name
- Database name
- User name
- Authentication type
Azure SQL Database server names take the form <ServerName>.database.windows.net.
LASER uses ‘Azure Active Directory - Interactive’ authentication to enable Contained Users to connect to Azure SQL Databases.
Few ODBC drivers currently support ‘Azure Active Directory - Interactive’ authentication, including ‘SQL Server Native Client 11.0’. A driver that does support it is ‘ODBC Driver 17 For SQL Server’, so this must be specified in your connection string.
Azure AD Interactive Authentication uses Azure Active Directory Multi-Factor Authentication technology to set up connection. In this mode, by providing the login ID, an Azure Authentication dialog is triggered and allows the user to input the password to complete the connection. The username is passed in the connection string.
Examples
Example connection string:
conn = "DRIVER={ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server}; SERVER=tcp:<Server Name>.database.windows.net; DATABASE=<Database Name>; UID=<username>@leeds.ac.uk; AUTHENTICATION=ActiveDirectoryInteractive"
Example Python function to upload a *.csv file to Azure SQL Database using pandas & sqlalchemy:
import pandas as pd
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
import urllib
def csv_to_sql(username, file, sql_server, sql_database, sql_schema, sql_tablename):
conn = urllib.parse.quote_plus("DRIVER={ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server};SERVER=tcp:" + sql_server + ";DATABASE=" + sql_database + ";UID=" + username + ";Authentication=ActiveDirectoryInteractive")
engine = create_engine("mssql+pyodbc:///?odbc_connect=%s" % conn, fast_executemany=True)
for chunk in pd.read_csv(file, chunksize=chunksize):
df = pd.DataFrame(chunk)
df.rename(columns=df.iloc[0])
df.to_sql(sql_tablename, con = engine, if_exists = "append", schema = sql_schema, index = False)